Secondary lithium batteries have the advantages of high single output voltage, long cycle life, large specific energy,
small size, low self-discharge, no memory effect, no pollution, and wide operating temperature range. They are widely
used in various fields. For lithium batteries, the charging method has a great impact on its performance, and a
reasonable charging method can extend the life of the lithium battery and improve the charging efficiency.

1. Theoretical basis
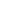
In 1972, American scientist J.A.Mas proposed that the battery has an optimal charging curve during charging:
I=I0e-αt, where; I0 is the initial charging current of the battery; α is the charge acceptance rate; t is the charging
time. The values of I0 and α are related to the battery type, structure and degree of oldness.
The current research on battery charging methods is mainly based on the best charging curve. As shown in
Figure 1, if the charging current exceeds this optimal charging curve, not only the charging rate cannot be
increased, but also the gas evolution of the battery will increase; if it is less than the optimal charging curve,
although it will not cause damage to the battery, it will extend Charging time reduces the charging efficiency.

Figure 1 Lithium battery charging characteristics
2. Charging method
There are many charging methods for lithium batteries, which can be divided into regular charging and fast
charging according to the charging efficiency. The conventional charging methods include constant current
charging, constant voltage charging, stage charging and intermittent charging, while fast charging includes pulse
charging and Reflex charging. Finally, intelligent charging is analyzed.
1. Constant current charging
According to the size of the charging current, constant current charging can be divided into fast charging, standard
charging and trickle charging. In the entire charging process, generally adjust the power supply charging voltage or
change the resistance value in series with the battery to maintain the battery charging current unchanged. This
method has the advantage of simple control and is suitable for charging a battery pack with multiple batteries
connected in series. The disadvantage is that the acceptable charging capacity of the lithium battery will gradually
decrease as the charging progresses, and the excessive charging current in the later stage of the charging will cause
bubbles in the battery to cause damage to the battery. Therefore, constant current charging is often used as a link in
stage charging.
2. Constant voltage charging
Constant voltage charging means that during the entire charging process, the charging voltage remains constant,
and the size of the charging current is automatically adjusted as the battery status changes. As the charging
progresses, the charging current gradually decreases. Compared with constant current charging, the charging
process is closer to the optimal charging curve, and the control is simple and the cost is low. The disadvantage is
that the charging time is long, and the battery charging current is too large in the early stage of charging, which
directly affects the life and quality of the lithium battery. Therefore, the constant voltage charging method is rarely
used alone, and only used when the charging power supply voltage is low and the current is large.
3. Constant current and constant voltage charging
Figure 2 shows the constant current and constant voltage charging curve. Before starting charging, first check the
battery voltage. If the battery voltage is lower than the threshold voltage (about 2.5V), the battery will be
trickle-charged with a small current of C/10 to make the battery voltage rise slowly; when the battery voltage
reaches the threshold voltage At this stage, it enters constant current charging. At this stage, the battery is quickly
charged with a larger current (0.5C ~ 1 C). The battery voltage rises quickly, and the battery capacity will reach
about 85% of its rated value; After rising to the upper limit voltage (4.2V), the circuit switches to constant voltage
charging mode, the battery voltage is basically maintained at 4.2V, the charging current gradually decreases, and
the charging speed slows down. This stage is mainly to ensure that the battery is fully charged. When the charging
current drops When it reaches 0.1C or 0.05C, it is judged that the battery is fully charged.

Figure 2 Constant current and constant voltage charging curve
Constant current and constant voltage charging avoids the problem of excessive charging current at the beginning
of constant voltage charging, and overcomes the prone to overcharging in the later stage of constant current
charging. The structure is simple and the cost is low. At present, the charging method of lithium batteries is widely
used . However, it cannot eliminate the polarization phenomenon during battery charging and affect the charging
effect.
4. Pulse charging
As shown in Figure 3, it is a pulse charging curve, which mainly includes three stages: pre-charge, constant current
charging and pulse charging.

Figure 3 Pulse charging curve
In the constant current charging process, the battery is charged with a constant current, and most of the energy is
transferred to the inside of the battery. When the battery voltage rises to the upper limit voltage (4.2V), it enters
the pulse charging mode: intermittently charge the battery with 1C pulse current. During the constant charging
time Tc, the battery voltage will continue to rise, and the voltage will slowly drop when the charging stops. When
the battery voltage drops to the upper limit voltage (4.2V), the battery is charged with the same current value, and
the next charging cycle begins, and the charging cycle continues until the battery is fully charged.
During the pulse charging process, the battery voltage drop speed will gradually slow down, and the charging stop
time T0 will become longer. When the constant current charging duty cycle is as low as 5% to 10%, the battery is
considered to be fully charged and the charging is terminated. Compared with the conventional charging method,
pulse charging can be charged with a larger current, and the concentration polarization and ohmic polarization of
the battery will be eliminated during the non-charging period, so that the next round of charging can proceed more
smoothly, and the charging speed is fast. The temperature change is small, and the impact on battery life is small, so
it is widely used at present. But its shortcomings are obvious: a power supply with current limiting function is
required, which increases the cost of pulse charging.
The pulse charging researched by C.K.Leong et al., each charging cycle lasts about 1s, first charge the battery in a
forward direction, then stop charging and discharge in the reverse direction for 20-30ms each. The positive pulse
current charges the battery, while the negative pulse current reduces the gas evolution from the electrode, which
can use a larger current to charge the battery quickly.
5. Intermittent charging method
Lithium battery intermittent charging method includes variable current intermittent charging method and variable
voltage intermittent charging method.
Variable current intermittent charging method
The variable current intermittent charging method was proposed by Professor Chen Tixian of Xiamen University. It
is characterized by changing the constant current charging to the voltage limiting variable current intermittent
charging. As shown in Figure 4(a), the first stage (and the main stage) of the variable-current intermittent charging
method is to first charge the battery with a larger current value, and stop charging when the battery voltage reaches
the cut-off voltage V0. At this time, the battery voltage is sharp decline.

Figure 4 Intermittent charging curve
After maintaining a period of stop charging, use a reduced charging current to continue charging. When the battery
voltage rises to the cut-off voltage V0 again, stop charging, so that the charging current will reduce the set cut-off
current value for several times (usually about 3 to 4 times). Then enter the constant voltage charging stage, charge
the battery with a constant voltage until the charging current decreases to the lower limit, and the charging ends. In
the main charging stage of the variable-current intermittent charging method, under the condition of limited
charging voltage, the intermittent method of gradually decreasing current is adopted to increase the charging
current, which speeds up the charging process and shortens the charging time. However, this charging mode
circuit is more complicated and expensive, and is generally only considered for high-power fast charging.
Variable voltage intermittent charging
On the basis of the variable current intermittent charging method, some people have studied the variable voltage
intermittent charging method. The difference between the two lies in the charging process of the first stage, which
replaces the intermittent constant current with the intermittent constant voltage. Comparing Figure 4 (a) and Figure
4 (b), it can be seen that constant voltage intermittent charging is more in line with the optimal charging curve. In
each constant voltage charging stage, due to the constant voltage, the charging current naturally decreases
exponentially, which conforms to the characteristic that the battery current acceptability rate gradually decreases
as the charging progresses.
6. Reflex fast charging method
The Reflex fast charging method is also known as the reflective charging method or "hiccup" charging method.
Each work cycle of this method includes three stages: forward charging, reverse instantaneous discharge and stop
charging. It solves the phenomenon of battery polarization to a large extent and speeds up the charging speed. But
reverse discharge will shorten the life of the lithium battery.
Sheng-Yuan Ou and Jen-Hung Tian conducted research on the Reflex fast charging method. The charging curve is
shown in Figure 5. In each charging cycle, the charging time of 2C current is first used as Tc of 10s, and then the
charging time is 0.5s Tr1, reverse discharge time is 1s Td, stop charging time is 0.5s Tr2, each charging cycle time is
12s. As the charging progresses, the charging current will gradually decrease. Experiments have proved that this
charging method can increase the charging time of a single lithium battery to 40 minutes, the battery temperature
only increases by 1.1 ℃, and the charging efficiency reaches 87.51%.

Figure 5 Reflex charging curve
7. Smart charging method
Intelligent charging is currently a more advanced charging method, as shown in Figure 6(a). Its main principle is to
apply du/dt and di/dt control technology to judge the battery charging state by checking the increase in battery
voltage and current. Track the acceptable charging current of the battery so that the charging current is near the
maximum acceptable charging curve of the battery all the time. In this way, the battery can be fully charged quickly
with little outgassing.

Figure 6 Smart charging
As shown in Figure 6(b), the neural network and fuzzy control are combined to develop a fuzzy neural network
controller and neural network model, and an intelligent charging control system is designed. It not only has the
characteristics of a fuzzy controller that is good at expressing human experience knowledge and strong reasoning
ability, but also has the characteristics of a neural network controller that learns knowledge directly from control
data and has strong learning ability. Experiments verify that the intelligent charging method has stable voltage
changes during the charging process and short charging time. Therefore, as one of the fuzzy adaptive control
schemes, the intelligent charging method will receive more and more attention in the future.